What Are the Cloud Computing Deployment Models?
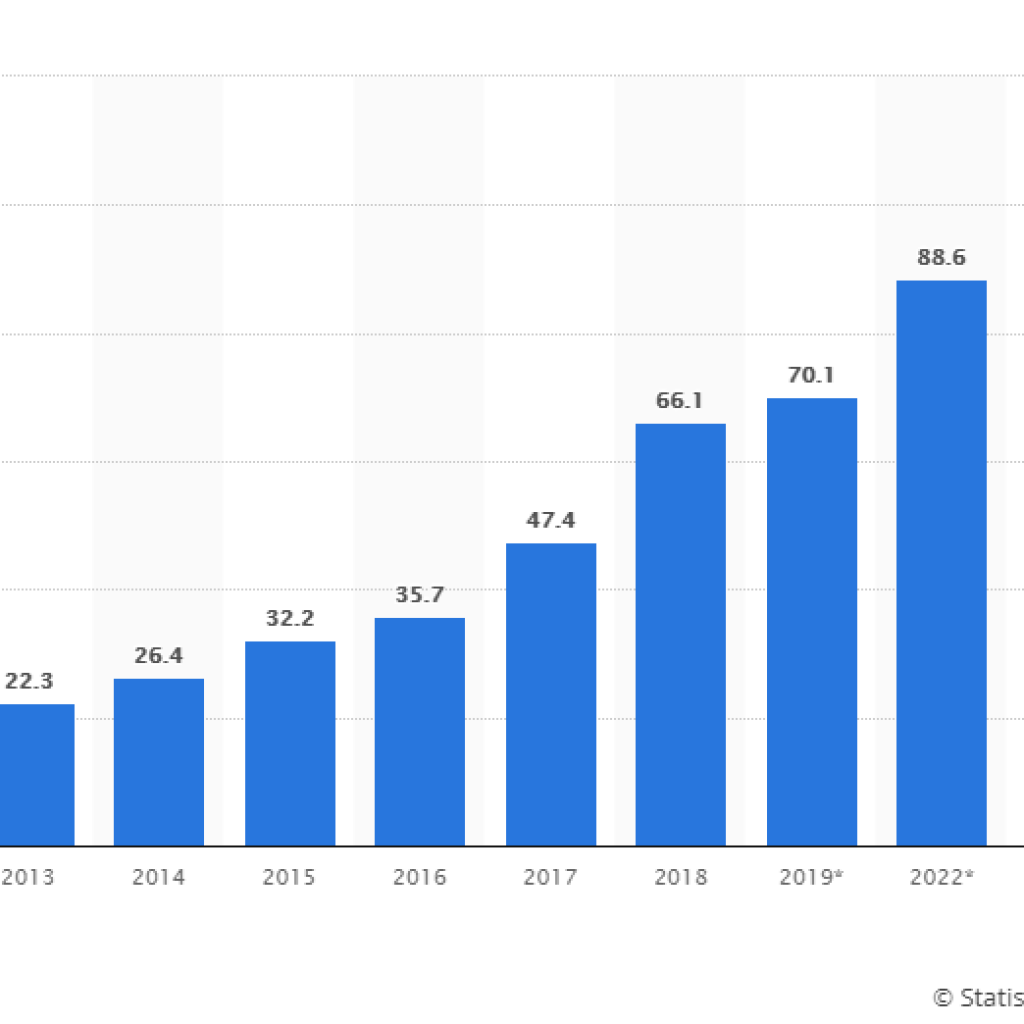
Cloud computing is on the rise. According to Statista, the annual spending on cloud IT infrastructure worldwide is growing by leaps with each passing year. In 2013, it was just $22.3 billion, almost tripling to $66.1 billion in 2018. It is expected to reach $70.1 billion in 2019.
The proliferation of cloud computing means that even small and medium-sized businesses are now moving their IT infrastructure to the cloud. Naturally, you would want to move your IT infrastructure to the cloud too.
However, you need the right cloud deployment model if you want to get the best out of cloud computing. Here are the most common cloud deployment models with their benefits and drawbacks.
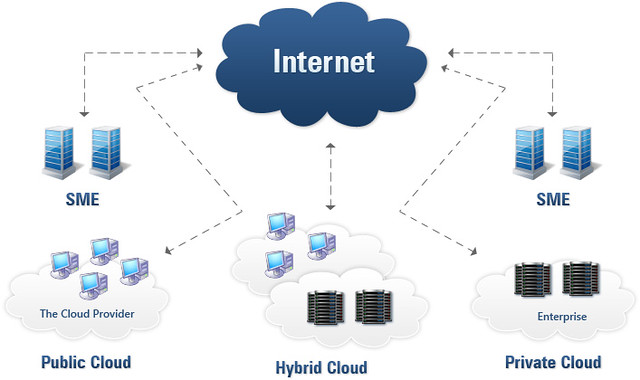
1. Public Cloud
This deployment model offers cloud computing services to users on a monthly or yearly subscription. The service providers own and operate the public cloud infrastructure to the general public.
a) Benefits
- Cost-Effective: Most public cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go subscriptions. In other words, you have to pay only for the services you are using. Also, as the underlying infrastructure is shared by all users, the cost of using the public cloud is relatively cheaper. It can help small and medium businesses save a considerable sum of money in the long run.
- Scalability: You can easily scale up or down the virtual machines or VMs within a public cloud system. As a result, you can add new VMs or shut down the old ones as per your changing business demand.
- No Maintenance or Management: If you are using an on-site data center or IT infrastructure, you already know that maintenance takes a large chunk of your budget. A public cloud can help you eliminate these costs.
- Convenient: You also don’t have to invest in setting up the cloud infrastructure as the service provider will take care of it. Most service providers also have several back-ups in different locations across the world.
b) Drawbacks
- Data Security and Privacy: Placing your critical information on the public cloud comes with risks. You have control over the operating system-level security configurations only. Everything else will be outside your physical control. Plus, hackers find the public cloud a more desirable target than other cloud models.
- Compliance Issues: Businesses handling sensitive customer data are often subject to strict legal regulations. If your business belongs to this category, the public cloud is not the right option for you.
c) Examples:
IBM Cloud, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
2. Private Cloud
Technically speaking, public and private clouds have very similar designs. However, unlike a public cloud, a private cloud is owned by a single user. The owner or a third-party or both may maintain its infrastructure.
a) Benefits
- Enhanced Security: As the data center architectures of a private cloud reside within the firewall, it is more secure. You also have complete control over security configurations. It is ideal for handling sensitive data.
- Higher Reliability: Compared to a physical data center, a private cloud is more reliable. It allows you to improve the allocation of your resources, making sure your business runs smoothly.
- Customization: As you have complete administrative control, you can customize your hardware and software resources as and when you want.
- Scalability: You can scale up or down your VMs, servers, and also the hardware to meet your business goals.
b) Drawbacks
- Cost: Cost is the main drawback. Not just the setup, but maintaining a private cloud infrastructure is also costly. You have to pay for everything. Outsourcing can reduce your costs to some extent, but the service provider will control the operating cost.
- Under-Utilization: Optimizing your resources can be a challenge as some of them may remain under-utilized. So, you may be paying for more services than you are actually using.
- Vendor Lock-In: Outsourcing a private cloud may lead to vendor lock-in. So, you may be forced to continue with the same service provider despite poor service and rising costs.
c) Examples:
Some of the well-known private cloud vendors are Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s (HPE) Helion Cloud Suite software, Dell EMC, IBM Cloud Managed Services, and Oracle, among others.
3. Community Cloud
In this deployment model, a community (businesses or any other organizations) with common concerns (security, privacy, and performance requirements) share the cloud infrastructure and resources. All users share the operating and maintenance costs. This relatively new option is gaining traction in the IT world.
a) Benefits
- Flexibility: It is a flexible cloud option without the downsides of a public cloud. You can scale up or down your infrastructure as you open new branches or close old ones.
- Reliability: You can replicate your critical data and applications, keeping them safe in case of a disaster. So, even if the computers are down, you can pull the data from the cloud and keep working.
- Security: As it is a tightly-knit community of users, this deployment model offers more reliable security compared to a public cloud. The centralized cloud facilitates secure data sharing within your organization.
b) Drawbacks
- Compliance Issues: Although secure, compliance can be particularly tricky in a community cloud as it is a distributed data system. Regulatory authorities may prohibit some businesses from using this cloud computing model.
- Limited Remote Access: You can allow your employees to remotely access the data. However, you may have to limit it to a handful of employees only for security reasons.
- Costs: While the costs are lower than that of a private cloud, they are certainly higher than a public cloud service.
- Slow Adoption: The community cloud concept is still in its infancy. Industries like media, healthcare, manufacturing, and energy can benefit from this model. But, adoption has been slower than expected.
c) Examples: Salesforce Community Cloud
4. Hybrid Cloud
As the name suggests, a hybrid cloud is a combination of any two or all three deployment models mentioned above. It tries to include the best features of each model.
For example, you can keep your sensitive data on a private cloud while sending less sensitive information to a public cloud. As an experienced provider of Cloud Management Services in Geneva, we have seen an increasing number of organizations choosing hybrid cloud.
a) Benefits
- Flexibility: You can keep your core data and workload on a private cloud. However, you can use the public cloud to deal with spikes in usage or workload.
- Cost-Effective: Although you will be investing in a private cloud setup, you will be paying for the public cloud only when needed. So, you can avoid the under or overutilization of your resources in the long run.
- Increased Efficiency: The highly scalable and flexible design ensures maximum workload management. This, in turn, translates into increased efficiency.
b) Drawbacks
- Costlier than Public Cloud: Although it proves cost-effective over time, hybrid cloud has higher initial setup costs than a public cloud system. You may also need to invest in on-premises hardware.
- Security: Security is better than a public cloud. But, you need to hire expert IT specialists to ensure the maximum security of your data.
c) Examples: Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform
Making the Right Choice
You can explore the incredible potential cloud computing can offer to your business. But, you will need to choose the right deployment model to make it a successful transition. Hopefully, learning about the pros and cons of the four leading cloud computing options should help. If you still have doubts, let’s continue this conversation. Drop us an email or drop a comment to talk about your cloud computing needs.